Article contents
The Number of Non-cyclic Sylow Subgroups of the Multiplicative Group Modulo n
Published online by Cambridge University Press: 08 June 2020
Abstract
For each positive integer n, let 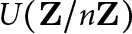 $U(\mathbf {Z}/n\mathbf {Z})$ denote the group of units modulo n, which has order
$U(\mathbf {Z}/n\mathbf {Z})$ denote the group of units modulo n, which has order  $\phi (n)$ (Euler’s function) and exponent
$\phi (n)$ (Euler’s function) and exponent 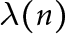 $\lambda (n)$ (Carmichael’s function). The ratio
$\lambda (n)$ (Carmichael’s function). The ratio 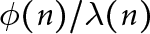 $\phi (n)/\lambda (n)$ is always an integer, and a prime p divides this ratio precisely when the (unique) Sylow p-subgroup of
$\phi (n)/\lambda (n)$ is always an integer, and a prime p divides this ratio precisely when the (unique) Sylow p-subgroup of 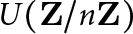 $U(\mathbf {Z}/n\mathbf {Z})$ is noncyclic. Write W(n) for the number of such primes p. Banks, Luca, and Shparlinski showed that for certain constants
$U(\mathbf {Z}/n\mathbf {Z})$ is noncyclic. Write W(n) for the number of such primes p. Banks, Luca, and Shparlinski showed that for certain constants 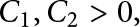 $C_1, C_2>0$,
$C_1, C_2>0$, 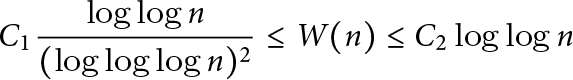 $$ \begin{align*} C_1 \frac{\log\log{n}}{(\log\log\log{n})^2} \le W(n) \le C_2 \log\log{n} \end{align*} $$
$$ \begin{align*} C_1 \frac{\log\log{n}}{(\log\log\log{n})^2} \le W(n) \le C_2 \log\log{n} \end{align*} $$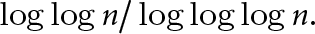 $\log \log {n}/\log \log \log {n}$.
$\log \log {n}/\log \log \log {n}$.
MSC classification
Information
- Type
- Article
- Information
- Copyright
- © Canadian Mathematical Society 2020
References
- 1
- Cited by


